In the dialogue builder, conditional blocks activate dialogue branches based on information in the conversation. This article explains what conditional blocks are and how to set them up for an advanced AI agent.
Understanding conditional blocks
Conditional blocks let you customize a conversation flow based on certain conditions. You can create conditional blocks based on:
- Parameters, which let you shape conversations based on information from your CRM platform, session data, or backend integrations.
- Segments, which let you shape conversations based on different types of customers.
Each conditional block represents a conditional statement that requires:
- A condition (a parameter or segment)
- An operator (such as “is” or “Is ANY of”)
- A value or set of values (including a null value)
When the conversation reaches the conditional block within a dialogue, the system evaluates the conditional statement as true or false. Based on the outcome, the conversation continues down the appropriate branch in the dialogue, as configured by you.
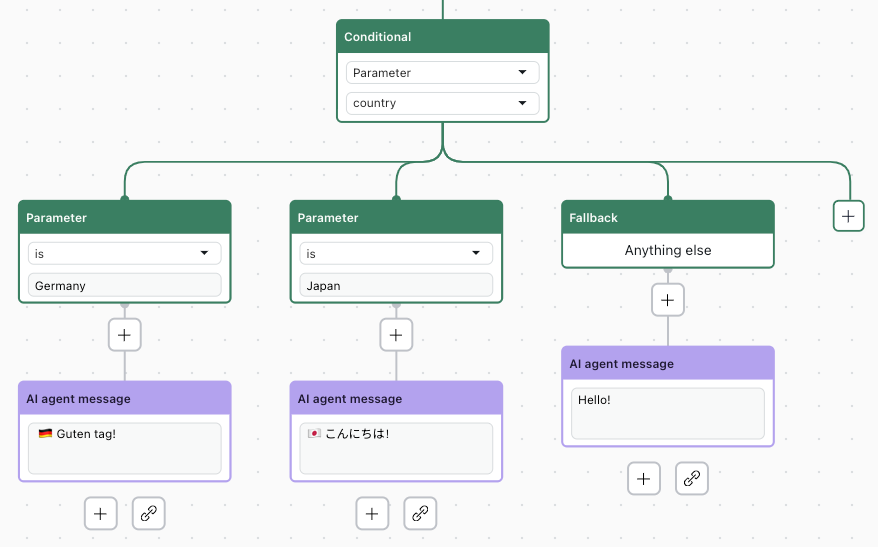
For example, you could configure the following conditional block:
- Parameter: country
- Operator: is
- Values: Germany, Japan
In this example, a customer reaching out to your AI agent will receive a different message based on their location, which is determined by the country parameter. Referencing the image below, if the customer is in:
- Germany, the conversation progresses down the left branch.
- Japan, the conversation progresses down the middle branch.
- Any other country, the conversation progresses down the right branch (the fallback
branch).
It’s important to understand and account for all possible scenarios when creating a conditional block and its resulting conversational branches, especially if you’re using values returned from an API.
Conditions are checked from left to right. Ensure that broader conditions you configure are positioned to the right of other, narrower conditions. The fallback condition, the broadest condition, is always positioned furthest right and can’t be moved.
Adding a conditional block to a dialogue
In the dialogue builder, you can add a conditional block to a dialogue. When you do, you can:
Configure a conditional block based on a parameter
Configuring a conditional block based on a parameter lets you shape conversations based on information from your CRM platform, session data, or backend integrations.
To configure a conditional block based on a parameter
- Open the dialogue builder for the dialogue you want to add a conditional block to.
- In the appropriate location in the dialogue, click the plus (+) icon and select
Conditional.
A set of blocks appear, including Conditional, Parameter, and Fallback.
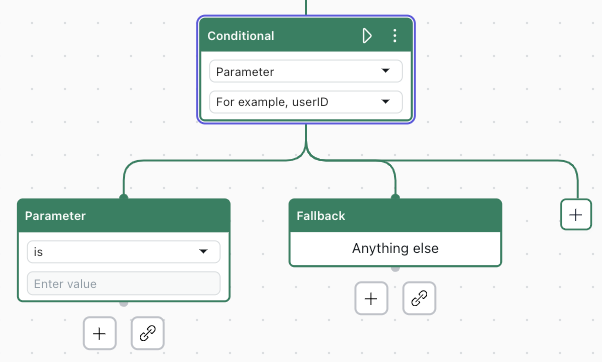
- In the Conditional block, use the second drop-down field to select the parameter you want to use.
If the parameter you want isn’t there, you can create an action to capture it.
- In the Parameter block, select the operator and enter the value to check for.
- Click the plus (+) icon below the Parameter block and configure the conversational
flow that should follow if the condition evaluates as true.Tip: You can even add another conditional block for increasingly tailored conversational flows.
- (Optional) Add another condition by clicking the plus (+) icon on the right.
An additional Parameter block is added to the left of the Fallback block.
Repeat steps 4 and 5. - Under the Fallback block, click the plus (+) icon and configure the conversational flow that should follow if none of the conditions are met.
Configure a conditional block based on a segment
Configuring a conditional block based on a segment lets you shape conversations based on different types of customers.
To configure a conditional block based on a parameter
- Open the dialogue builder for the dialogue you want to add a conditional block to.
- In the appropriate location in the dialogue, click the plus (+) icon and select
Conditional.
A set of blocks appear, including Conditional, Parameter, and Fallback.
- In the Conditional block, use the first drop-down field to select Segment.
The Parameter block changes to a Segment block.
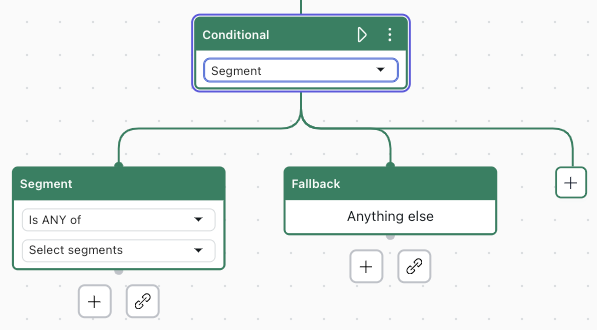
- In the Segment block, select the:
- Operator (Is ANY of, Is NOT ANY of, Is ALL of)
- Segments to check for
- Click the plus (+) icon below the Segment block and configure the conversational
flow that should follow if the condition evaluates as true.Tip: You can even add another conditional block for increasingly tailored conversational flows.
- (Optional) Add another condition by clicking the plus (+) icon on the right.
An additional Segment block is added to the left of the Fallback block.
Repeat steps 4 and 5. - Under the Fallback block, click the plus (+) icon and configure the conversational flow that should follow if none of the conditions are met.